OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Volatility and Tick Size Data
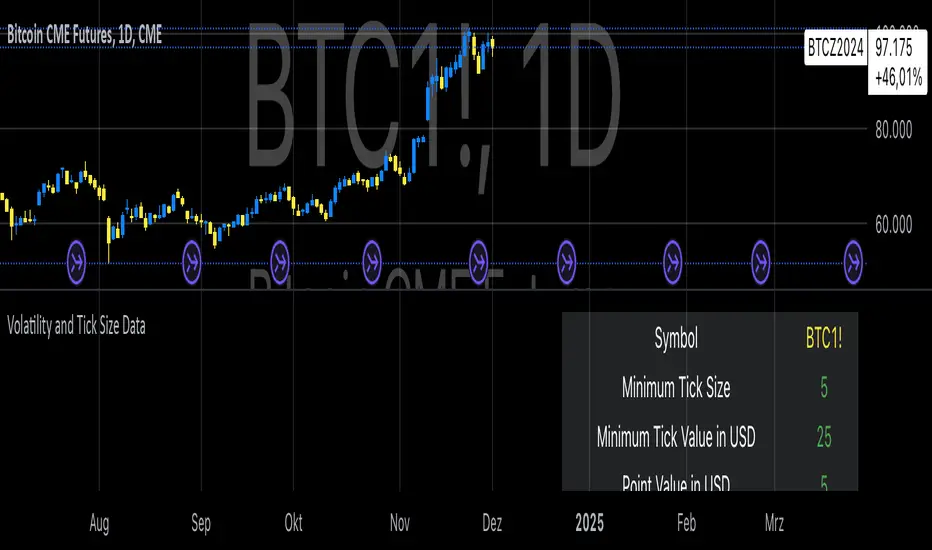
This indicator, titled "Tick Information & Standard Deviation Table," provides detailed insights into market microstructure, including tick size, point value, and standard deviation values calculated based on the True Range. It helps visualize essential trading parameters that influence transaction costs, risk management, and portfolio performance, including volatility measures that can guide investment strategies.
Why These Data Points Are Important for Portfolio Management
Tick Size and Point Value:
Tick size refers to the smallest possible price movement in a given asset. It defines the granularity of the price changes, affecting how precise the market price can be at any moment. Point value reflects the monetary value of a single price movement (one tick). These two data points are essential for understanding transaction costs and for evaluating how much capital is at risk per price movement. Smaller tick sizes may lead to more efficient pricing in high-frequency trading strategies (Hasbrouck, 2009).
Reference: Hasbrouck, J. (2009). Empirical Market Microstructure. Foundations and Trends® in Finance, 3(4), 169-272.
Standard Deviations and Volatility:
Standard deviation measures the variability or volatility of an asset's price over a set period. This data point is critical for portfolio management, as it helps to quantify risk and predict potential price movements. True Range and its standard deviations provide a more comprehensive measure of market volatility than just price fluctuations, as they include gaps and extreme price changes. Investors use volatility data to assess the potential risk and adjust portfolio allocations accordingly (Ang, 2006).
Reference: Ang, A. (2006). Asset Management: A Systematic Approach to Factor Investing. Oxford University Press.
Risk Management:
The ability to quantify risk through metrics like the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd standard deviations of the true range is essential for implementing risk controls within a portfolio. By incorporating volatility data, portfolio managers can adjust their strategies for different market conditions, potentially reducing exposure to high-risk environments. These volatility measures help in setting stop-loss levels, optimizing position sizes, and managing the portfolio’s overall risk-return profile (Black & Scholes, 1973).
Reference: Black, F., & Scholes, M. (1973). The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities. Journal of Political Economy, 81(3), 637-654.
Portfolio Diversification and Hedging:
Understanding asset volatility and transaction costs is critical when constructing a diversified portfolio. By using the standard deviations from this indicator, investors can better identify assets that may provide diversification benefits, potentially reducing the overall portfolio risk. Moreover, the point values and tick sizes help assess the cost-effectiveness of various assets, enabling portfolio managers to implement more efficient hedging strategies (Markowitz, 1952).
Reference: Markowitz, H. (1952). Portfolio Selection. The Journal of Finance, 7(1), 77-91.
Conclusion
The Tick Information & Standard Deviation Table provides critical market data that informs the risk management, diversification, and pricing strategies used in portfolio management. By incorporating tick size, point value, and volatility metrics, investors can make more informed decisions, better manage risk, and optimize the returns on their portfolios. The data serves as an essential tool for aligning asset selection and portfolio allocations with the investor's risk tolerance and market conditions.
Why These Data Points Are Important for Portfolio Management
Tick Size and Point Value:
Tick size refers to the smallest possible price movement in a given asset. It defines the granularity of the price changes, affecting how precise the market price can be at any moment. Point value reflects the monetary value of a single price movement (one tick). These two data points are essential for understanding transaction costs and for evaluating how much capital is at risk per price movement. Smaller tick sizes may lead to more efficient pricing in high-frequency trading strategies (Hasbrouck, 2009).
Reference: Hasbrouck, J. (2009). Empirical Market Microstructure. Foundations and Trends® in Finance, 3(4), 169-272.
Standard Deviations and Volatility:
Standard deviation measures the variability or volatility of an asset's price over a set period. This data point is critical for portfolio management, as it helps to quantify risk and predict potential price movements. True Range and its standard deviations provide a more comprehensive measure of market volatility than just price fluctuations, as they include gaps and extreme price changes. Investors use volatility data to assess the potential risk and adjust portfolio allocations accordingly (Ang, 2006).
Reference: Ang, A. (2006). Asset Management: A Systematic Approach to Factor Investing. Oxford University Press.
Risk Management:
The ability to quantify risk through metrics like the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd standard deviations of the true range is essential for implementing risk controls within a portfolio. By incorporating volatility data, portfolio managers can adjust their strategies for different market conditions, potentially reducing exposure to high-risk environments. These volatility measures help in setting stop-loss levels, optimizing position sizes, and managing the portfolio’s overall risk-return profile (Black & Scholes, 1973).
Reference: Black, F., & Scholes, M. (1973). The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities. Journal of Political Economy, 81(3), 637-654.
Portfolio Diversification and Hedging:
Understanding asset volatility and transaction costs is critical when constructing a diversified portfolio. By using the standard deviations from this indicator, investors can better identify assets that may provide diversification benefits, potentially reducing the overall portfolio risk. Moreover, the point values and tick sizes help assess the cost-effectiveness of various assets, enabling portfolio managers to implement more efficient hedging strategies (Markowitz, 1952).
Reference: Markowitz, H. (1952). Portfolio Selection. The Journal of Finance, 7(1), 77-91.
Conclusion
The Tick Information & Standard Deviation Table provides critical market data that informs the risk management, diversification, and pricing strategies used in portfolio management. By incorporating tick size, point value, and volatility metrics, investors can make more informed decisions, better manage risk, and optimize the returns on their portfolios. The data serves as an essential tool for aligning asset selection and portfolio allocations with the investor's risk tolerance and market conditions.
Script open-source
Dans l'esprit TradingView, le créateur de ce script l'a rendu open source afin que les traders puissent examiner et vérifier ses fonctionnalités. Bravo à l'auteur! Bien que vous puissiez l'utiliser gratuitement, n'oubliez pas que la republication du code est soumise à nos Règles.
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
Clause de non-responsabilité
Les informations et publications ne sont pas destinées à être, et ne constituent pas, des conseils ou recommandations financiers, d'investissement, de trading ou autres fournis ou approuvés par TradingView. Pour en savoir plus, consultez les Conditions d'utilisation.
Script open-source
Dans l'esprit TradingView, le créateur de ce script l'a rendu open source afin que les traders puissent examiner et vérifier ses fonctionnalités. Bravo à l'auteur! Bien que vous puissiez l'utiliser gratuitement, n'oubliez pas que la republication du code est soumise à nos Règles.
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
Clause de non-responsabilité
Les informations et publications ne sont pas destinées à être, et ne constituent pas, des conseils ou recommandations financiers, d'investissement, de trading ou autres fournis ou approuvés par TradingView. Pour en savoir plus, consultez les Conditions d'utilisation.