OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Mis à jour CT Reverse MACD Cross
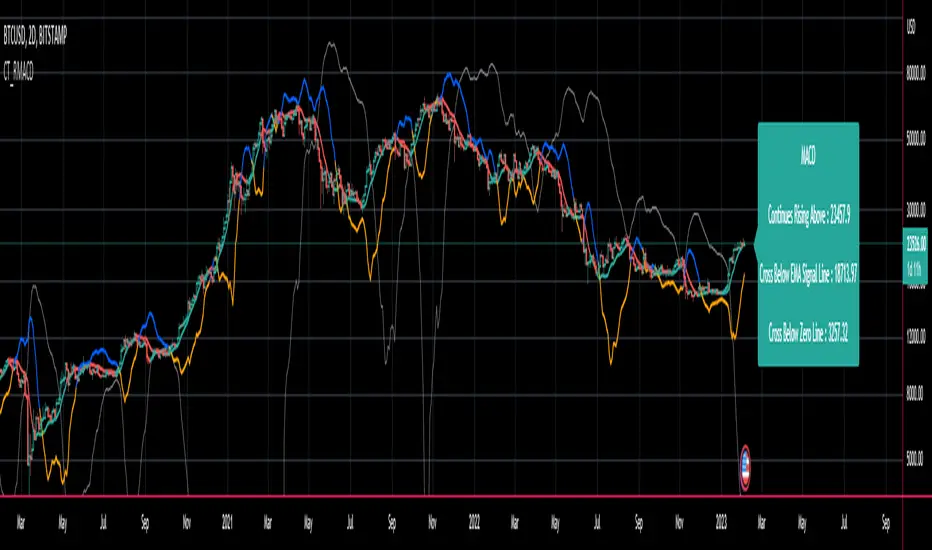
Introducing the Reverse MACD Cross
MACD.... short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of stock prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s.
It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price.
Prior work by Johny Dough showed how we can compute the price level required to make the MACD stay at its current level,
and also how to compute the price level required for the MACD to cross the zero line.
I have brought that idea to it logical conclusion for the MACD by creating a new function which also computes the price level required to cross the MACD with its signal line.
This allows the user to quickly see all of the most relevant information from the MACD and the actual price levels where the indicator will change its posture.
The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the closing price.
These three series are:
MACD.... short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of stock prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s.
It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price.
Prior work by Johny Dough showed how we can compute the price level required to make the MACD stay at its current level,
and also how to compute the price level required for the MACD to cross the zero line.
I have brought that idea to it logical conclusion for the MACD by creating a new function which also computes the price level required to cross the MACD with its signal line.
This allows the user to quickly see all of the most relevant information from the MACD and the actual price levels where the indicator will change its posture.
The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the closing price.
These three series are:
- the MACD series proper shown here in blue
- the "Signal Line" or "average" series shown here in red
- the "Divergence" series which is the difference between the two shown here as a histogram.
There is also usually a baseline set at zero.
The MACD series is the difference between a "fast" (short period) exponential moving average (EMA), and a "slow" (longer period) EMA of the price series.
The average series (signal line) is an EMA of the MACD series itself.
The MACD indicator thus depends on three parameters, namely the time periods of the three EMAs.
The notation "MACD ( a, b, c )" usually denotes the standard indicator where the MACD series is the difference of EMAs with characteristic times a and b, and the average series is an EMA of the MACD series with characteristic time c.
There is an infobox which displays...- Whether the MACD is falling or rising
- the price level which will make the MACD to change from rising to falling or vice versa
- the price level which will cause the MACD to cross the signal line
- the price level which will cause the MACD to cross the zero line
The most commonly used values are 12 for the fast, 26 for the slow, and 9 for the signal line, that is, MACD ( 12, 26, 9 ).
The MACD and average series are customarily displayed as continuous lines in a plot whose horizontal axis is time oscillating above and below a zero line, whereas the divergence is commonly shown as a bar graph / histogram.
A fast EMA responds more quickly than a slow EMA to recent changes in a stock's price.
By comparing EMAs of different periods, the MACD series can indicate changes in the trend of a stock.
It is claimed that the divergence series can reveal subtle shifts in the stock's trend.
Since the MACD is based on moving averages, it is a lagging indicator. As a future metric of price trends, the MACD is less useful for stocks that are not trending (trading in a range) or are trading with unpredictable price action.- Whether the MACD is falling or rising
Notes de version
Corrected code description and minor function errorNotes de version
Switched plot order to bring lines to the front of the histogramNotes de version
Created and added SMA signal line cross function by request.. Added
- optional SMA signal line
- optional SMA based histogram
Modified textbox info and coloring logic for clarity
Notes de version
Final tidy upNotes de version
Added Zeroline cutoff feature to the reverse functions in order to alleviate autofocus chart issues.Removed transp variable from plot functions in advance of its planned obsolescence.
Notes de version
Upgraded to Pinescript Version 5Added plot settings options.
Added settings headings.
Script open-source
Dans l'esprit TradingView, le créateur de ce script l'a rendu open source afin que les traders puissent examiner et vérifier ses fonctionnalités. Bravo à l'auteur! Bien que vous puissiez l'utiliser gratuitement, n'oubliez pas que la republication du code est soumise à nos Règles.
You may contact me on Krown's Crypto Cave Discord: discord.gg/W9ettX54DF My Discord username is The Caretaker.
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
Clause de non-responsabilité
Les informations et publications ne sont pas destinées à être, et ne constituent pas, des conseils ou recommandations financiers, d'investissement, de trading ou autres fournis ou approuvés par TradingView. Pour en savoir plus, consultez les Conditions d'utilisation.
Script open-source
Dans l'esprit TradingView, le créateur de ce script l'a rendu open source afin que les traders puissent examiner et vérifier ses fonctionnalités. Bravo à l'auteur! Bien que vous puissiez l'utiliser gratuitement, n'oubliez pas que la republication du code est soumise à nos Règles.
You may contact me on Krown's Crypto Cave Discord: discord.gg/W9ettX54DF My Discord username is The Caretaker.
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
Clause de non-responsabilité
Les informations et publications ne sont pas destinées à être, et ne constituent pas, des conseils ou recommandations financiers, d'investissement, de trading ou autres fournis ou approuvés par TradingView. Pour en savoir plus, consultez les Conditions d'utilisation.